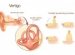
Sapta Dhatu in Ayurveda
From Anatomy point of view, dhatu refers to tissue. In Rasa Shastra, dhatu stands for the minerals. The seven tissues or more precisely, dhatus are important from anatomical point of view. They are rasa, rakta, mamsa, medas, asthi, majja and shukra. From human anatomy point of view, they are better described as plasma, blood, muscle, fat or adipose tisue, bone, bone-marrow and seminal fluid. Basic understanding of dhatus is vital to understand the underlying pathology of the disease. When a dosha or biological humour enters a particular dhatu, a genuine understanding of the tissue or the dhatu helps the Ayurvedic practitioner for prediction of the symptoms of the diseases. It is helpful in providing hint to the best possible treatment.
According to Ayurvedic system of medicine, the seven dhatus are chiefly responsible for the immunity. Ayurvedic system of medicine follows a very rational and specific method for treatment for diseases having relation to the particular dhatus. The growth and existence of the human body is dependent on these seven dhatus. These seven dhatus are composed of five elements or panchmahabhutas. When there is an imbalance or disequilibrium in functioning of the dhatus, the result is the manifestation of the disease.
When the food we eat is digested and is converted into three portions:
- The gross undigested food is converted into waste prodcuts (faeces);
- The middle is converted in one of the tissues or Dhatus,
- The subtlest form gets converted into ojasa (sara of the seven dhatu) or the immunity.
As per rule and regulation, food we eat is firstly converted into Rasa. Once there is formation of Rasa, the remaining gets converted into Rakta. Once there is formation of Rakta, the remaining gets converted into Mamsa. Once there is formation of Mamsa, the remaining gets converted into Meda. Once there is formation of Meda, the remaining gets converted into Asthi. Once formation of Asthi is over, the remained gets converted into Majja. Once there is formation of Majja, the remaining gets converted into Shukra.
Dhatvagni
All the seven element tissues of the body contain their own agni to metabolize the nutrients supplied to them through channels of circulation.
- Rasagni in the Rasa Dhatu or plasma
- Raktagni in the Rakta Dhatu or blood
- Mamsagni in the Mamsa Dhatu or muslce
- Medagni in the Meda Dhatu or fat
- Asthyagni in the Asthi Dhatu or bone
- Majjagni in the Majja Dhatu or bone-marrow
- Shukragni in the Shukra Dhatu or reproductive fluid.
Rasa-Plasma
According to Ayurvedic system of medicine, rasa represents the first dhatu. Rasa is the major and primary constituent of the human body. Rasa represents the fluids (extra cellular and intracellular parts) of the human body and it mainly concerned with nourishment and strengthening the blood. Once the process of digestion of the food is complete, it gets converted into a liquid (chyle) which undergoes transformed into blood tissue.